728x90
반응형
오늘은 자바의 static 변수와 static 메소드에 대해 알아보려고 합니다.
1. static 변수
변수 앞에 static이라는 키워드를 붙이면, 자바는 메모리 할당을 딱 한 번만 하게 됩니다. 따라서 메모리 사용에 이점이 있죠.
따라서 static으로 선언한 변수를 참조할 땐, 같은 곳의 메모리 주소를 바라보기 때문에 static 변수의 값을 공유할 수 있습니다. 아래 예제를 통해 이 말이 무엇인지 설명하겠습니다.
함수를 선언하고 객체가 해당 함수를 참조할 때마다 카운터가 올라가는 코드를 구현한다고 가정해 보겠습니다.
- static을 사용하지 않고 구현을 하면 다음과 같은 결과를 얻게 됩니다.
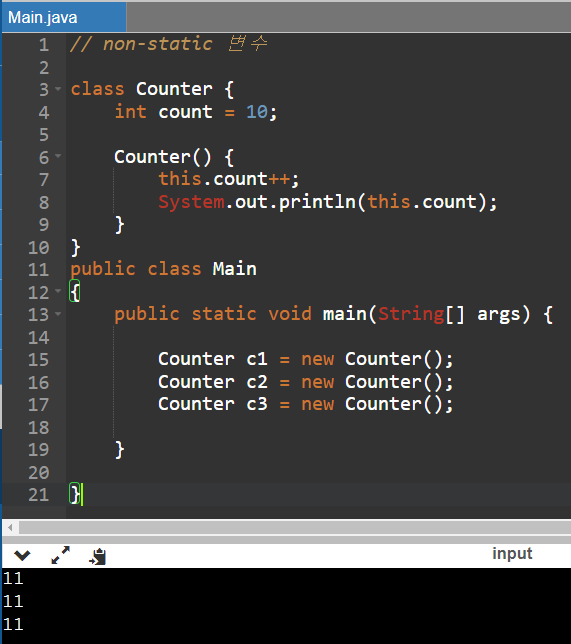
// non-static 변수
class Counter {
int count = 10;
Counter() {
this.count++;
System.out.println(this.count);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter c1 = new Counter();
Counter c2 = new Counter();
Counter c3 = new Counter();
}
}매번 새로운 count 변수를 메모리에 할당하기 때문에, 여러 번 Counter함수에 접근해도 11이라는 결과만 출력됩니다.
- 다음은 static을 포함한 코드입니다.
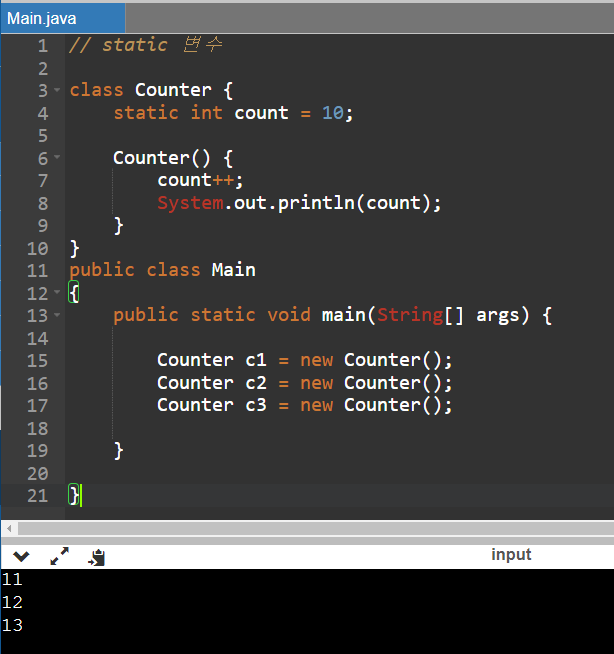
// static 변수
class Counter {
static int count = 10;
Counter() {
count++; // static 변수라서 this 삭제
System.out.println(count);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter c1 = new Counter();
Counter c2 = new Counter();
Counter c3 = new Counter();
}
}
이 경우에는 count변수가 딱 한번 선언되기 때문에, Counter 클래스의 객체가 생성될 때마다 count변수 값이 증가되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
2. static 메소드
메소드 앞에 static 키워드를 붙이면, 객체 없이도 클래스를 통해 메서드를 직접 호출할 수 있습니다. 위의 카운트 예제를 가져와서 static 메소드를 추가해보겠습니다.
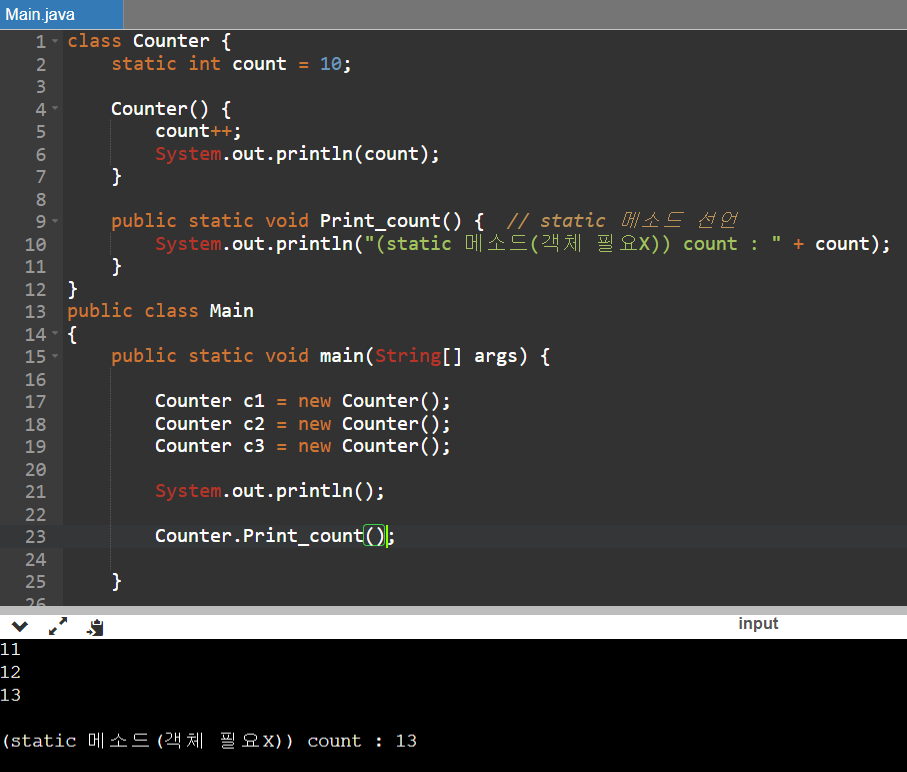
class Counter {
static int count = 10;
Counter() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void Print_count() { // static 메소드 선언
System.out.println("(static 메소드(객체 필요X)) count : " + count);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter c1 = new Counter();
Counter c2 = new Counter();
Counter c3 = new Counter();
System.out.println();
Counter.Print_count();
}
}Counter 클래스의 Print_count() 메소드를 보면, static이라는 키워드가 붙어있습니다.
이처럼 static 메소드를 붙이면, main 함수에서 객체 없이 "Counter.Print_count()"처럼 접근이 가능합니다.
다른 static 메소드 예제를 보겠습니다.
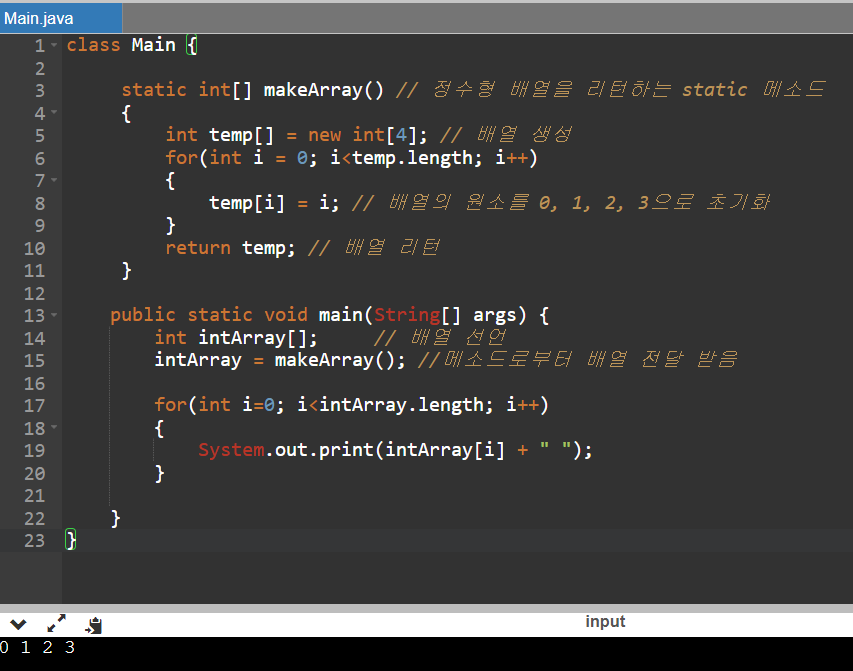
이번 예제는 배열을 생성하고, 리턴해주는 static 메소드입니다.
class Main {
static int[] makeArray() // 정수형 배열을 리턴하는 static 메소드
{
int temp[] = new int[4]; // 배열 생성
for(int i = 0; i<temp.length; i++)
{
temp[i] = i; // 배열의 원소를 0, 1, 2, 3으로 초기화
}
return temp; // 배열 리턴
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intArray[]; // 배열 선언
intArray = makeArray(); // 메소드로 부터 배열을 전달 받음
for(int i=0; i<intArray.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(intArray[i] + " ");
}
}
}객체 생성 없이 바로 makeArray()메소드에 접근하는 걸 확인할 수 있습니다.
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JDK 다운, PATH 환경 설정 - 공부하는 도비 (0) | 2023.01.26 |
|---|---|
| 자바 상속 기초 4) 메소드 overloading - 공부하는 도비 (0) | 2022.04.02 |
| 자바 상속 기초 3) 메소드 overriding - 공부하는 도비 (0) | 2022.04.02 |
| 자바 상속 기초 2) super - 공부하는 도비 (0) | 2022.04.02 |
| 자바 상속 기초 1) - 공부하는 도비 (0) | 2022.04.02 |